In today’s very competitive manufacturing landscape, ensuring efficiency and productivity is a necessity for businesses to stay competitive.
Every business is now under pressure to produce more products with higher quality, faster, yet with fewer resources, and in practice, this can be a major challenge. Whether you are running a small production line or a large-scale factory, you are on this same journey for increased efficiency.
With that being said, efficient production lines are the foundation of any successful manufacturing process, but achieving and maintaining high levels of production line efficiency can be easier said than done.
This is where this guide comes in.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore actionable insights and practical strategies to improve your production line efficiency. Throughout this guide, we’ll discuss various aspects of production line efficiency improvement, including:
- Important KPIs to measure production line efficiency
- Evaluating the current state of your production line
- Potential challenges in optimizing your production line
- Different methods for improving production line efficiency
- Measuring and monitoring production lines to ensure continuous improvement.
And more.
By the end of this guide to production line efficiency improvement, you’d have a comprehensive understanding and a toolkit of strategies to improve your manufacturing operation, increase productivity, reduce costs, and achieve success.
Without further ado, let us delve into this guide.
Understanding Production Line Efficiency
Production line efficiency, in a nutshell, is the ratio of the production line’s output to its input.
It measures how effective a production line is in utilizing materials (and other resources), minimizing waste, and maximizing its output at any given time.
In short, production line efficiency is a measure of how well a production line performs in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall productivity. A high level of production line efficiency means that the line is producing a high quantity of products (with a consistent level of quality) and with a minimum of waste.
Measuring and optimizing production line efficiency is important for a number of reasons, including:
- More effectively meeting customer demands: an efficient production line allows the company to deliver high-quality products in a more timely manner, meeting customer demands and ensuring customer satisfaction.
- Optimize resources: the more efficient a production line is, the more efficient it will be at utilizing resources and minimizing waste. Production line efficiency helps businesses optimize their usage of materials, labor, and time, effectively reducing operational costs.
- Improved productivity: improving production line efficiency enables the business to produce more output with the same resources (or the same output with fewer resources), improving its productivity. Ultimately, higher productivity will also translate to higher profitability for the business.
- Improve employee morale: when employees know they are working with an efficient production line, they are more likely to experience more satisfaction in their work. This can lead to increased employee productivity and a decrease in turnover.
How to Measure Production Line Efficiency: Important KPIs
Now that we’ve understood the significance of measuring production line efficiency, how can we actually measure it?
To accurately measure production line efficiency, we can use a number of key performance indicators (KPIs), including:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
OEE is one of the most relevant metrics used to measure a piece of equipment’s actual output compared to its maximum potential output. A production line, as we know, is a collection of equipment, so OEE can be used to measure the production line’s efficiency.
OEE is calculated by multiplying three factors: Availability x Performance x Quality.
Availability: refers to the percentage of time the equipment is available for use during a scheduled production time. It is calculated by dividing the total time the equipment is actually available (scheduled production time - downtime) by the total scheduled production time.
Performance: the percentage of time the equipment is operating at its most optimal speed. Calculated by the following formula: (total parts produced / ideal cycle time) / scheduled operating time. Ideal cycle time is the time required to produce a single part/product under optimal conditions.
Quality: this factor refers to the percentage of good parts produced during the scheduled operating time. Calculated by dividing the total quantity of good parts produced by the total parts produced.
For example, if the availability score is 90%, the performance score is 95%, and the quality score is 99%, then the OEE would be calculated as follows:
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality = 90% x 95% x 99% = 85.65% - Work-in-Progress (WIP)
WIP refers to the number of unfinished parts or products in various stages of the manufacturing process. A high quantity of WIP indicates that there are inefficiencies/bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.
Managing WIP effectively is crucial in any production line to ensure a smooth and efficient workflow.
- Defect rate
The percentage of defective products or parts produced by the production line. A high defect rate indicates that there are inefficiency issues or bottlenecks that may need to be addressed. - Throughput
Throughput refers to the rate at which products are manufactured and delivered within a designated timeframe. A high level of throughput indicates that the production line is working at an optimal capacity with efficient output. - Cycle time
Cycle time refers to the amount of time it takes to produce a single product (or part) in the manufacturing process—a single full cycle of production, from start to finish. A high cycle time may indicate that there are inefficiencies or bottlenecks in the manufacturing process. - Takt time
Takt time refers to the rate at which the product or part needs to be produced to meet the customer’s (or client’s) demands.
A production line is said to be operating “at takt time” when it is producing parts or products at a rate that is just sufficient to meet these demands.
This is not an exhaustive list, and there are definitely more KPIs and metrics you can use to measure your production line’s current efficiency. Yet, they are among the most important ones you should monitor.
In the next section, we will discuss how to assess your production line’s current state of efficiency, so you can plan your optimization strategy.
Assessing Current Production Line State of Efficiency
The first step in improving a production line’s efficiency is to evaluate its current state, and below are the key things to consider.
1. Identifying bottlenecks via observation
A ‘bottleneck” is any point in the manufacturing process that experiences a slowdown or a complete halt.
Bottlenecks can occur due to a variety of reasons, for example:
- Lack of raw materials/delay in supply
- Equipment failure
- Equipment needing resting time
- Human error
- Operators unavailable
And more.
Identifying—and then eliminating—bottlenecks is a critical step in improving production line efficiency.
Observe your current workflow, and gather feedback from workers and supervisors to identify bottlenecks and potential areas for improvement.
2. Analyzing workflow to identify inefficiencies
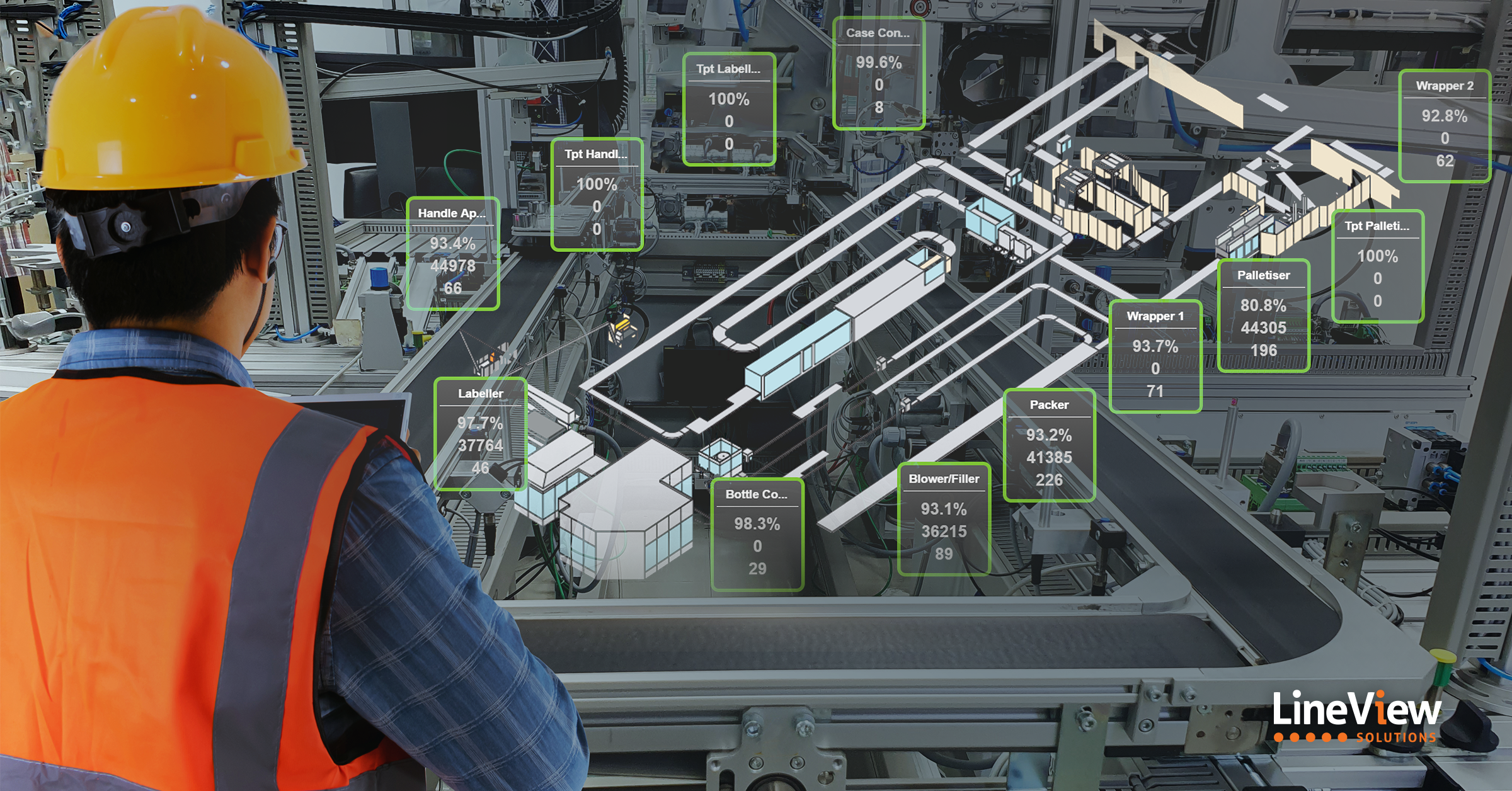
Leverage production line balancing solutions like LineView to map out your production line’s workflow and state of equipment efficiencies.
Carefully document each step from the very start to the end, and then analyze this workflow to:
- Identify task dependencies: analyze the sequence of tasks in the workflow and their dependencies (i.e., whether a task needs to be completed before another can start.) Identify any unnecessary or redundant tasks. Look for opportunities to minimize delay or waiting times, for example, by reordering the sequence of tasks.
- Analyze workload balance: assess how workloads are distributed across different workstations or tasks, and look for any imbalances. Redistribute tasks by using workload balancing strategies to optimize how you use your resources.
- Look for overlaps and handoffs: Identify areas where multiple workstations or tasks are involved in completing a single process. Overlaps or handoffs may increase the chances of delays and errors. Make sure there is clear communication between tasks and workstations.
- Identify non-value-added activities: identify redundant activities like excessive rework, unnecessary inspections, etc., that consume time without adding value. Eliminate or reduce these activities to streamline the workflow.
- Assess equipment utilization: evaluate how equipment and tools are optimized at each stage of the production process. Identify underutilization, inefficiencies (i.e., poorly maintained or outdated tools), and equipment downtime, and explore opportunities to optimize equipment utilization.
- Engage with frontline workers: conduct surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather your workers’ feedback. Try to understand their perspectives by involving them in the analysis process.
- Measure time and motion: use time and motion study methods to capture data about the time needed to perform specific tasks and/or movements within the process. Motion and study analysis can help you streamline your workflow, reduce unnecessary movements, and improve overall efficiency.
3. Establishing baseline performance metrics
Once you have identified bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the production line, the next crucial step is to establish baseline performance metrics.
These are the reference points you’ll use to keep track of and monitor the effectiveness of any implemented changes, and here are the basic steps you should take:
- Determine KPIs: determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are most relevant to your manufacturing process and most critical to your overall goals. Consider metrics like cycle time, throughput, etc., that we’ve discussed in the previous section.
- Measure and record current performance levels: this is important data to collect that will serve as a benchmark to compare future improvements.
- Establish a data collection system: use data collection and analytics solutions to establish an accurate and consistent method for data collection, so you can ensure metrics are accurately measured.
4. Gathering data and conducting performance audits
Once you’ve established a data collection system, then the obvious next step is to start collecting data and auditing your production line’s performance.
Consider the following steps when conducting your performance audits:
- You can use manual data collection methods (i.e., observations), sensors, or software solutions to capture relevant metrics. Experiment with different methods to identify the most appropriate/accurate ones for different data points.
- Once you’ve identified the appropriate data collection method, establish standardized procedures to collect data on each data point. Make sure the data collection process is reliable and consistent, so you can maintain data accuracy and integrity.
- When collecting data manually (i.e., via observation), consider using a random sampling technique. Randomly select samples from different time periods or production runs to ensure representative data collection.
- Involve relevant stakeholders (i.e., operators, supervisors, managers) in the performance audit process. Their perspectives may provide valuable context and insights into identifying inefficiencies, and may help generate improvement ideas.
Potential Challenges when Improving Production Line Efficiency
In attempting to improve production line efficiency, there are various challenges that you may need to consider and address as soon as possible:
- Resistance to change
It’s natural for people to dislike change, and this is why implementing changes to achieve better efficiency in your production line often encounters resistance from employees and stakeholders who have grown to be too accustomed to the status quo.
To overcome this resistance, effective communication is critical. Be proactive in communicating the benefits of the improved efficiency, and commit to providing proper support and training to help them adapt. - Limited budgets and resources
Improving production line efficiency may require investment in new machinery, technologies, and employee training/education programs, among others, which can be expensive.
Limited budgets and resources can pose a challenge, especially for small or financially constrained companies. It is essential to carefully plan and prioritize these investments and actively explore options for more cost-effective solutions. - Complexity of processes
The processes in the production line that need to be optimized can be complex: each may involve multiple steps with different coordination requirements and interdependencies.
Analyzing and understanding these complexities is critical if you really want to achieve efficiency, but at the same time, this can be very challenging in practice. It’s important to conduct thorough process/workflow mapping and analysis as the foundation for the improvement initiatives. - Balancing efficiency and quality
While our goal here is to achieve better efficiency, we should be careful that the increased inefficiency doesn’t come at the expense of product quality.
Finding the sweet spot between efficiency and quality is highly critical. To do so, it’s essential to establish strict quality control measures and continuous monitoring with production line monitoring software to ensure that the improvement initiatives do not lead to an increase in errors or product defects. - Managing change effectively
Improving production line efficiency often involves significant changes in roles, responsibilities, and even processes. All these changes can be disruptive.
It’s very important to manage change effectively, including having a comprehensive plan for implementing changes, clear communication, ensuring stakeholder engagement, and providing training/support to employees.
If we fail to successfully navigate these changes, achieving improved efficiency can be very difficult to do. - External factors
We should also consider external factors such as market demands, regulatory changes, or disruptions in the supply chain that may occur during the improvement/optimization initiatives.
It’s critical for the company to remain agile during the initiatives and quickly respond to these external factors by adjusting their strategies and executions accordingly.
Strategies for Improving Production Line Efficiency
Now that we’ve conducted a thorough performance audit to assess the current state of your production line, in this section, we will explore strategies that can enhance your production line efficiency.
We will divide the improvement initiatives into three major categories:
- Optimizing and streamlining processes
- Enhancing equipment and technology
- Empowering the workforce
Below, we will explore each of them in greater detail, starting with the first one.
1. Optimizing and streamlining processes
Streamlining the production line’s workflow and its processes is critical to improving production line efficiency.
There are several key focuses here: ensuring smoother flow throughout the production line, eliminating bottlenecks, and reducing cycle times. We will achieve these goals by adopting these strategies:
- Implement lean manufacturing principles: lean manufacturing is a set of principles focusing on eliminating waste and unnecessary steps in the production process. Some of the key manufacturing principles include:
- Value stream mapping: identifying all the steps involved in the manufacturing process and analyzing the value of each step to the final product. Steps that do not add value can be eliminated.
- Kanban: Kanban is a system of production that uses visual cues to determine when tasks are needed. Work/task is only done when it’s needed and is not pushed onto the production line to prevent bottlenecks.
- Just-in-time (JIT): another system of production in which materials and components are only ordered when they are needed. This principle helps to reduce inventory and logistics costs to improve efficiency.
- Reducing waste: waste in a production process refers to anything that does not add value to the product, which can be scraps, defects, unnecessary motion, reworks, etc. Identifying and reducing waste is crucial for improving efficiency, and the company should perform a comprehensive waste analysis to be able to adopt appropriate waste reduction strategies (i.e., 5S methodology, Kanban, Just-in-time, etc.)
- Standardizing work procedures: standardization plays a critical role in ensuring consistent and efficient operations. It’s critical to establish clear work procedures and document them in SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) to minimize process variations, reduce delays/errors, and improve the overall production line efficiency.
2. Enhancing equipment and technology efficiency
The efficiency of a production line will strongly depend on the equipment and technology used in the system. To enhance equipment and technology efficiency, we can adopt the following strategies:
- Conducting regular maintenance and inspections: to ensure optimal performance and minimize unexpected downtime (i.e., failures, breakdown), it’s critical to establish a preventive maintenance schedule, utilize machine downtime tracking software and perform regular inspections. Address any issues identified in the inspection process promptly to reduce downtime and even extend their lifespan.
- Upgrading machinery and tools: outdated machinery and equipment will naturally lose efficiency. Evaluate the performance and efficiency of your current equipment, and upgrade to newer/more advanced machinery and tools as needed.
- Implement automation: automation, for example, the use of robotics, can improve speed, consistency, and precision, especially in repetitive tasks like material handling or assembly. Automated equipment and systems can speed up cycle times and reduce human error, leading to improved production line efficiency.
3. Empowering the workforce
Another piece in the puzzle in driving production line efficiency is a well-trained and motivated workforce.
You can adopt the following strategies to enhance employee capabilities and overall productivity:
- Invest in training and skill development opportunities: providing adequate training and skill development opportunities is critical for improving production line efficiency. Consider offering training on new technologies, cross-functional skills, and process improvements.
- Fostering a culture of continuous improvements: encourage employees to participate in improvement-related initiatives, provide platforms that encourage continuous improvements, and facilitate open communication channels.
- Performance incentives and recognition programs: implementing recognition and performance initiative programs can help to motivate employees to improve their efficiency and productivity.
Wrapping Up
Improving production line efficiency is essential for any manufacturer or business that wants to stay competitive amidst the saturated business landscape.
By following the actionable tips we’ve shared in this article, companies can achieve significant improvements in their production line efficiency, which will result in reduced costs, increased productivity, and enhanced customer/client satisfaction.
However, implementing the necessary changes to achieve improved production line efficiency can be very challenging in practice, including when measuring and tracking progress. This is where LineView can be your valuable partner in implementing production line efficiency initiatives.
With LineView’s state-of-the-art tools, you can gain real-time visibility into your production line performance, enabling you to make informed decisions to drive continuous improvement.
